Numerous individuals take preventative measures against influenza by receiving an annual flu shot. This vaccine, which may be administered through injection or nasal spray, has been shown to cut your risk of contracting influenza by as much as 60%. Reliable Sourcing. The flu vaccination usually only causes minimal side effects. Yet sometimes, they may be rather serious. Know what to anticipate after getting the flu vaccination. Some flu vaccination multidose vials include thimerosal, a preservative made from mercury. It can stop the spread of bacteria and other pathogens. The CDC confirms that using thimerosal in vaccinations is safe and seldom results in adverse reactions. People who have concerns about thimerosal can request a thimerosal-free vaccination. This data from the CDC details the thimerosal content of presently available flu vaccinations.
The Most Frequent Adverse Effects
Flu shots often only cause mild cases of the most prevalent adverse effects. They are the same in both mature adults and developing infants.
Injection Site Reaction
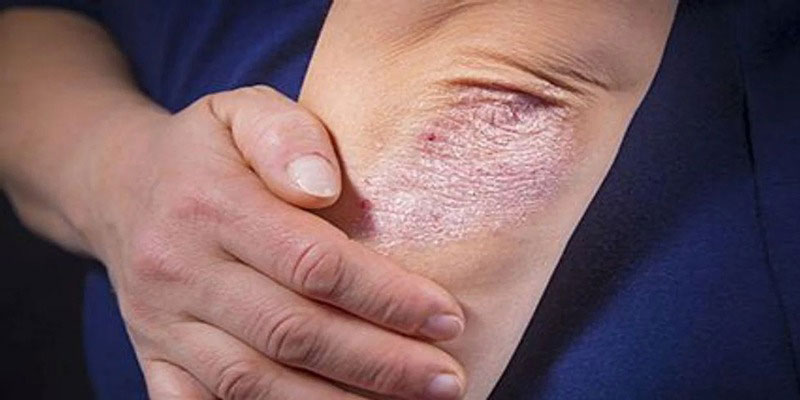
The flu shot's most frequent negative impact is a localized response at the injection site (usually the upper arm). Swelling, redness, warmth, and pain are all possible side effects of the injection. These results often have a short duration (less than two days). Take some ibuprofen before having the injection to lessen the pain.
Various Aches And Pains, Such As A Headache

You may have soreness and stiffness in your muscles after getting an injection. This often occurs on day one and resolves itself by day two. Assisting your pain with medication is a good idea. Using NSAIDs like acetaminophen and ibuprofen to alleviate the discomfort caused by vaccines has been met with mixed reviews. There is evidence to show that certain drugs may moderate or entirely dampen the protective effects of the vaccination. Acetaminophen and ibuprofen were shown not to affect the body's immune response toward the flu vaccination in a trial including youngsters. The results of other studies are inconsistent. The question of whether or not these medicines should be avoided remains open.
Fainting Or Dizziness
The flu vaccination has been linked to fainting and dizziness. The duration of these results should be at most two days. Please inform your doctor if you experience lightheadedness or fainting after receiving injections.
You could also try the following:
- After getting the shot, you need to sit for a bit.
- eating anything either before or following the injection
Fever
A frequent reaction to the flu vaccine is a mild fever, defined as a temperature of 101 degrees Fahrenheit (38 degrees Celsius) or less. In terms of adverse effects, a modest temperature is regarded to be on the mild side. Expect it to clear up in a couple of days. Take ibuprofen or acetaminophen if the fever is bothersome. As mentioned above, acetaminophen and other NSAIDs like ibuprofen and naproxen have been called into question. The use of these drugs raises concerns that they may reduce the effectiveness of immunizations. Unfortunately, there are no definite results from the studies conducted thus far.
Chances Of Getting Sick From The Flu

The likelihood of contracting influenza increases for several demographics. The CDC Reliable Source recommends giving priority to these populations during times of flu vaccination scarcity. Age, race, and pre existing diseases are a few variables that increase the likelihood of a negative outcome.
Particular age groups are at higher risk, and they include:
- Infants and toddlers
- Young people under the age of 18 who use aspirin or other salicylate-containing drugs
- individuals aged 65 and above
People of the following ethnicities are at greater risk:
- Originating from the Americas, Native Americans
- Locals from Alaska
Complications from the flu are more likely to occur in people with the following conditions:
- Asthma, heart disease, and lung disease
- problems affecting the endocrine system, which may lead to long-term complications in the urinary tract and liver, and kidneys, such as diabetic Mellitus
- epilepsy, stroke, and cerebral palsy are only a few examples of the chronic neurological and neurodevelopmental diseases
- diseases of the blood that won't go away for a long time, like sickle cell anemia
- Diseases of the metabolism that persist throughout time
There are more groups of persons that are at a higher risk, and these include:
Persons who are immunocompromised owing to illness (which includes cancer, HIV, as well as AIDS) and otherwise long-term steroid drug usage, pregnant women, people with something like a BMI of 40 or above, People who seem to be morbidly obese
Conclusion
Like any other medication, the flu vaccination may have unwanted side effects. Symptoms are short-lived and moderate the majority of the time. After receiving a vaccination, it's common to feel a little off. This demonstrates that your immune system is learning to defend itself against the illness after vaccination. Of course, only some have adverse effects. Compared to the flu's severity or complications, these possible side effects are minor. Common adverse effects of the flu vaccine include soreness at the injection site and headaches. In 1–2 days, you should feel back to normal after getting a flu vaccination. Don't hesitate to see your doctor if the unpleasant effects continue beyond this time frame. The majority of flu shot adverse effects are easily treated with over-the-counter medications. There are almost seldom any major adverse effects.